|
For those suffering from gait disturbance, dementia, and urinary issues caused by idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: At our clinic, we offer minimally invasive shunt surgery that can lead to symptom improvement. We provide clear explanations and offer tailored treatments based on each patient's condition. In particular, we focus on addressing peripheral symptoms such as decreased mental activity due to dementia and urinary incontinence, aiming for improvement through surgery. The surgical procedure takes approximately 30 minutes, and the hospitalization period, including rehabilitation, is about one week. Even in cases where the diagnosis is challenging or symptoms have progressed, please feel free to consult us. This disease is still relatively unknown to the general public, but we have the experience and expertise to handle it at our clinic. At our clinic, we utilize the latest technology and techniques to perform minimally invasive shunt surgery, ensuring that even elderly patients can undergo the procedure with confidence. Prioritizing the health and safety of our patients, we prioritize surgical approaches that involve incisions in the lumbar and abdominal regions without touching the brain. This minimizes the burden and risks associated with the surgery, allowing for a smoother and safer procedure. We carefully counsel each patient, taking into consideration their preferences and individual conditions, and propose the most suitable surgical approach accordingly.
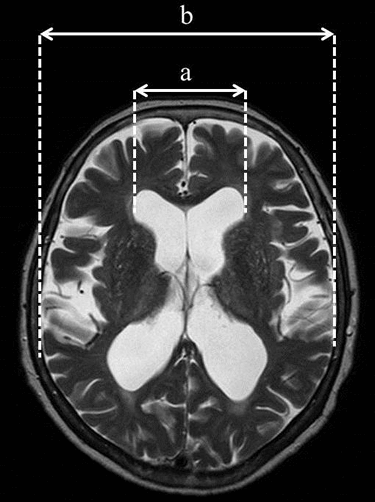
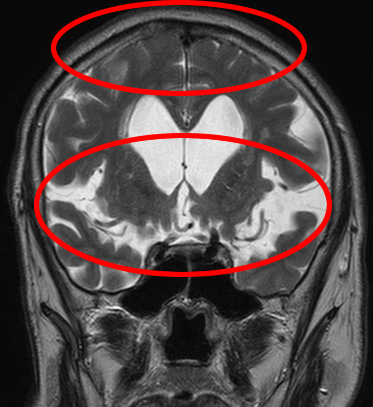
¨@The surgical procedure@@https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31860824/ In iNPH, shunt surgery offers the potential for improvement in gait disturbance and a remarkable enhancement in quality of life. Additionally, if iNPH is the underlying cause, surgery may also lead to improvements in dementia, which is generally considered difficult to treat. At our clinic, we perform shunt surgery that typically takes around 30 minutes, and the hospitalization period, including rehabilitation, is approximately one week. We prioritize the health and safety of our patients, and our dedicated team of specialized physicians and staff provide comprehensive support. If you are facing challenges related to iNPH, we encourage you to consult with our clinic. ¨@Preoperative gait disturbance@https://youtu.be/qhM4-a2ROgw We are experienced in handling patients with difficult diagnoses and advanced symptoms. We provide clear explanations and are here to address any concerns you may have. Please feel free to consult with us without hesitation. iNPH (Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus) is a relatively unknown condition that primarily affects individuals aged 65 and older, causing gait disturbance, dementia, and urinary frequency. It is a rare disease where intracranial pressure remains normal, but specific symptoms manifest. Due to the possibility of underdiagnosis and inadequate treatment, our clinic has specialized physicians who diagnose and treat iNPH. If you are experiencing symptoms and concerns, please don't hesitate to consult with us. ¨ For more information on Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus, please refer to the following link.@https://inph.jp/ ¡Triad symptoms of iNPHThe three main symptoms of iNPH are gait disturbance, dementia, and urinary incontinence, with gait disturbance being the most characteristic and potentially improvable symptom. It is characterized by a reduced stride length, decreased leg lifting, and wide-based gait, and it can manifest from the early stages of the disease. The gait can resemble that of Parkinson's disease. At our clinic, we specialize in shunt surgery for iNPH, aiming to improve gait disturbance. A person in their 70s fell at home and was taken to the emergency room, but CT scans showed no serious injuries. However, two months later, they fell again and were diagnosed with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH). 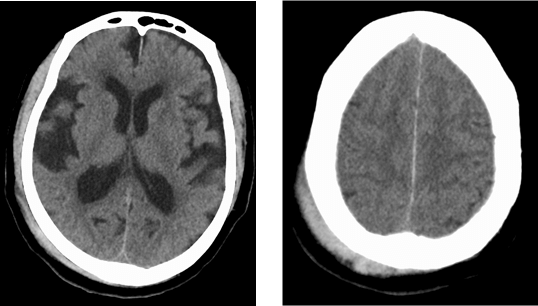 Dementia exhibits frontal lobe cortical impairment, leading to symptoms such as slowed thinking and attention deficits. Patients may become apathetic or indifferent, with slowed or decreased spontaneous behavior, often resulting in a vague state of mind. This is the CT image of an individual in their 80s who sought medical attention due to concerns about dementia. Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) was suspected, and the symptoms improved following shunt surgery. 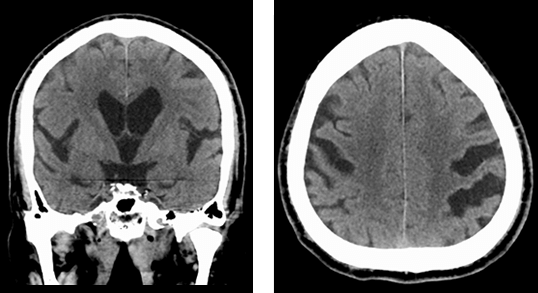 In idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH), urinary incontinence occurs less frequently compared to gait disturbance and dementia, and it is usually accompanied by urinary frequency. However, there are cases where urinary dysfunction is the only symptom, so it is necessary to diagnose it in conjunction with other signs. Additionally, the appearance of urinary incontinence can lead to a decreased quality of life for the individual and their family, highlighting the importance of early detection and treatment. ¡Regarding iNPH examinationsiNPH is diagnosed through examinations such as CT and MRI scans, which examine abnormalities in the brain. In this condition, a part of the brain called the "ventricles" is enlarged compared to normal, and the degree of enlargement is assessed using specialized measurement methods. One commonly used indicator in this measurement is the Evans index, and a value of 0.3 or higher indicates ventricular enlargement. The diagnostic guidelines for iNPH also emphasize the importance of ventricular enlargement as a crucial piece of diagnostic information.
The tap test is a highly effective diagnostic examination for iNPH. It involves collecting cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to evaluate the degree of symptom improvement and confirm the suitability for shunt surgery. The procedure is performed using a thin needle, resulting in minimal discomfort and high safety. The results of the tap test provide crucial information for predicting the success rate of shunt surgery. It is recommended for individuals with suspected iNPH to undergo a tap test to assess their condition. ¡Minimally invasive shunt surgeryAppropriate surgery is essential for the treatment of iNPH. In our clinic, we recommend the use of LP (lumboperitoneal) shunt surgery, which is minimally invasive and effective. This procedure involves incisions in the lumbar and abdominal regions and offers advantages over VP (ventriculoperitoneal) shunt surgery. LP shunt surgery does not require direct penetration of the brain, does not necessitate general anesthesia, and typically takes about 30 minutes to complete. Additionally, it can be performed under spinal or local anesthesia, allowing communication with the patient immediately after surgery.
¨@https://publish.m-review.co.jp/book/detail/978-4-7792-2672-4 ¡Message from the attending physicianDear patient, When it comes to the health of our loved ones, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial if any concerning symptoms or discomfort arise. As we age, conditions such as gait disturbances, cognitive decline, and urinary issues may occur. However, it's important not to underestimate these symptoms, as doing so might lead to overlooking potentially treatable diseases. Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (iNPH) is a gradually progressive condition, and early detection is key. If you suspect iNPH or experience related symptoms, I recommend undergoing tests such as tap test to aid in diagnosis. Following an accurate diagnosis, shunt surgery can be performed, offering the possibility of improvement in gait disturbances, cognitive decline, and urinary problems. To enhance quality of life, it is essential to prioritize early diagnosis and treatment. Remember, taking proactive measures for early detection and treatment can make a significant difference in improving your loved one's health and overall well-being. Please do not hesitate to reach out to us if you have any concerns or wish to schedule a consultation. We are here to support you and help you regain control of your health. Sincerely,
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|